Decorators
Decorators can implement various functions for controllers and are generally used in conjunction with controllers.
Usage:
import {FireCatController, Get, Request, Context} from "fire-cat";
export class HomeController extends FireCatController {
@Get('/') // Define routes for controllers
@Request() // Merge the obtained user input parameters into the request
index(ctx: Context) {
ctx.body = 'hello world'
}
}export const Auth1 = function () {
return FireCatDecorator.registerImplement(async (ctx, next) => {
// Simulate parsing of user data
ctx.state.userInfo = {
id: 1,
name: 'fake',
some: 'bar'
}
await next()
})
}Types of Decorators
Decorators are categorized into different types according to their functions:
Request Decorators
These decorators handle certain processes during requests, such as@Request()and request interceptors. This is equivalent toKoajs'middleware.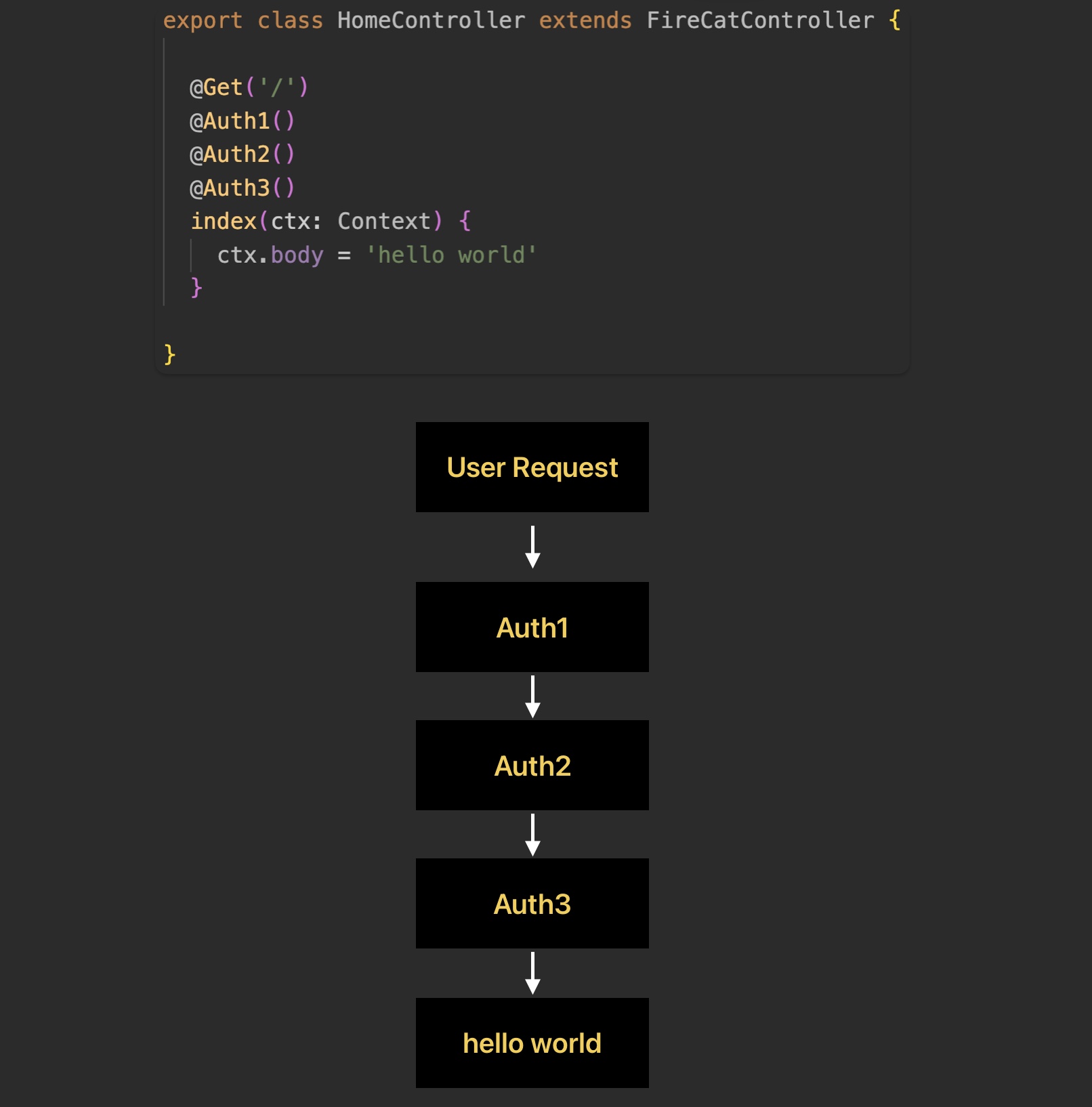
Route Decorators
These decorators are used to define routes.Definition Decorators
These decorators perform operations on the current controller after being defined, such as the@Get()route decorator.
Route Decorators
Route decorators are provided by the system to assign route request paths to methods within controllers.
Usage:
import {FireCatController, Get, Request, Context} from "fire-cat";
export class HomeController extends FireCatController {
@Get('/') // Define the route for the controller
@Request()
index(ctx: Context) {
ctx.body = 'hello world'
}
}Definition Decorators
Definition decorators perform operations on the current controller after being defined, such as the @Get() route decorator.
